Week 3 Lab
from Electronic Technologies for Art
Contents
Analog Input
- now... driving it with input data, instead of with a loop.
- File->Sketchbook->Analog->AnalogInput
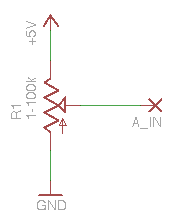
Potentiometer
- A_IN can be any of the Analog pins (0-5) on your Freeduino.
- Q: What will the voltage at A_IN be? What are the upper and lower values?
- The important part of this sketch is the line where the microprocessor reads the analog input:
val = analogRead(potPin); // read the value from the sensor
- Q: Looking at the Arduino help for that function (
analogRead()), what do you think the valuevalwill be for those highest and lowest voltages at your A_IN pin? - Q: How can you verify your guess? Try and verify your values, in some plausible manner. Anything goes!!
other loads
photoresistor
- taking the photoresistor from your 147A kit, it has a resistance of ~160k - ~10k (depending on your lighting conditions)
- Q: With the same R2 resistor (10k) from above, replacing R1 with the photoresistor, what range of voltages (and corresponding data values) would you expect to see at your A_IN pin?
- Q: Using methods you invented above, verify your data readings.
strain gauge
flex sensor
Analog Output
LED Dimming
- File->Sketchbook->Examples->Analog->Fading
analogWrite(ledpin, value); // sets the value (range from 0 to 255)
PWM (pulse width modulation)
- lights, fading
<youtube v="62gWVWCyw_w" loop="true"/>
ultrasonic rangefinder
Analog Output, Again
Other things you can control.
Motor Speed Control
- Basic motor control (DC motors) see week 5
Sound, Tone Generation
- sounds, tone generation
Bonus Section
- Cadsoft EaglePCB - the program to make schematics and design PCB layout.